TIL
TIL - 2024/06/13
기석김
2024. 6. 13. 13:00
Error와 Exception
Java에서는 Compile 오류, Runtime 오류 두 종류가 있다. Compile 오류는 IDE에서도 미리 알 수 있기 때문에
잡아내기 쉽지만, Runtime은 해결하기 까다롭다. Java에서 Runtime 오류는 Error와 Exception이 있다.
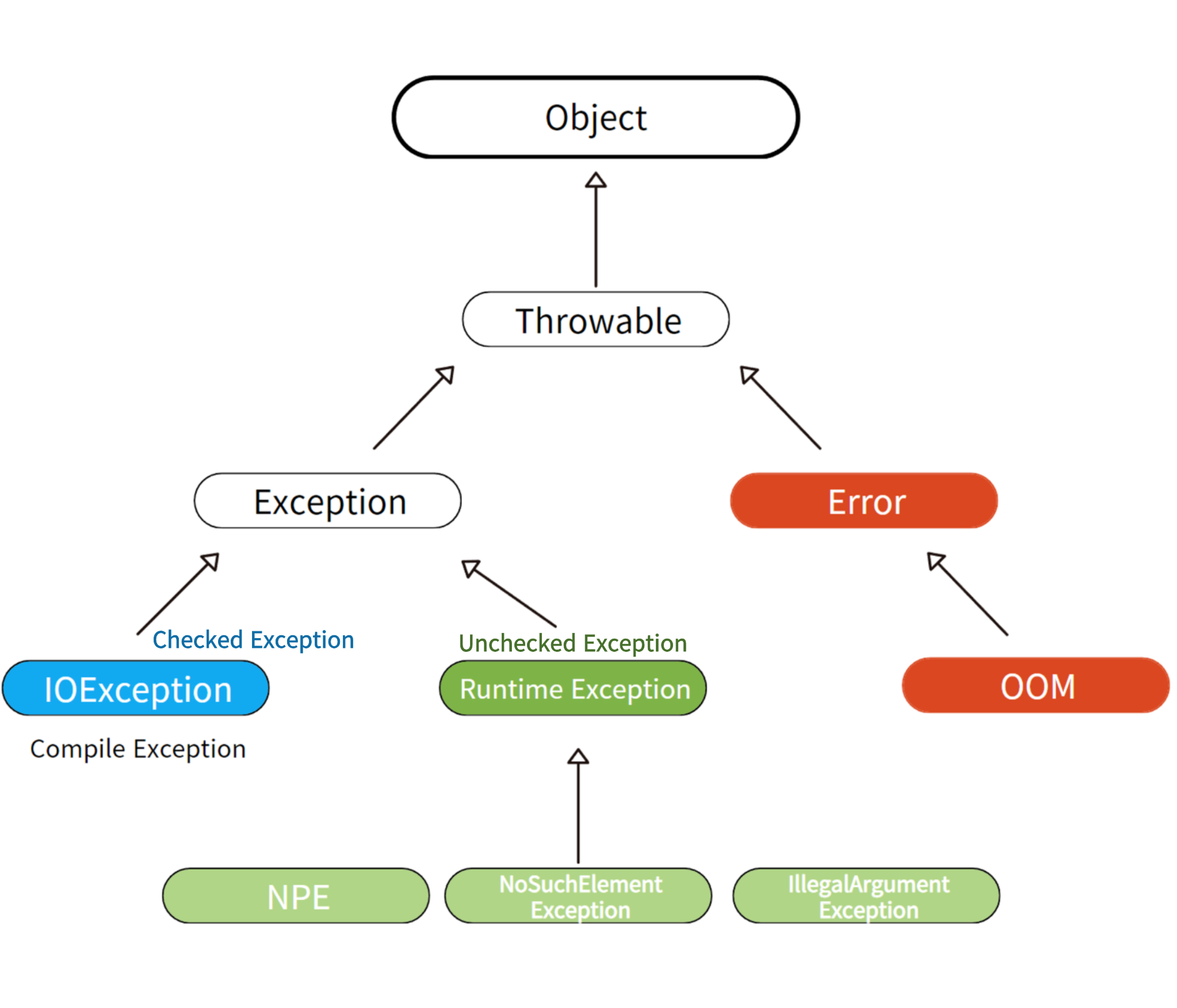
- Error
- 코드로 복구되지 않는 오류
- 개발자가 직접 Error를 catch하면 안된다. 해결할 수 없다.
- ex) OOM(OutOfMemory Error) - 실행중 메모리 부족
- 코드로 복구되지 않는 오류
- Exception
- 개발자가 직접 처리할 수 있는 오류
- ex) NPE(NullPointerException), IllegalArgumentException
- Compile Exception
- Checked Exception 이다.
- Compiler 가 확인한다.
- Runtime Exception
- Unchecked Exception 이다.
- Compile 후 실행(Runtime)단계에 발생하는 Exception
- Exception 상속관계
- 상속 개념은 Exception에도 적용된다.
- catch 를 통해 예외를 잡으면 하위 Exception들도 모두 catch 한다.
- Throwable Class를 catch 하면 안된다. Error Class도 모두 catch되기 때문
- 즉, Exception 하위 클래스만 예외 처리를 하면 된다.
Checked Exception, Unchecked Exception
Checked Exception
- Exception class를 상속받으면 checked Exception이 된다.
- Compiler가 체크한다.
- Checked Exception은 발생한 예외를 개발자가 명시적으로 처리해야 한다.
- catch 혹은 throws 로 처리한다.
- throws 했다면 이후에 꼭 catch 해야한다.
- 만약, 처리하지 않으면 Compile 오류가 발생한다.
- catch 혹은 throws 로 처리한다.
Unchecked Exception
- RuntimeException과 하위 Exception
- 말그대로 Compiler가 체크하지 않는다.
- Unchecked Exception은 발생한 예외를 개발자가 명시적으로 처리하지 않아도 된다.
- throws를 생략할 수 있다. Checked Exception은 꼭 처리 해야됨
Checked Exception, Unchecked Exception
Checked Exception
- Exception class를 상속받으면 checked Exception이 된다.
- Compiler가 체크한다.
- Checked Exception은 발생한 예외를 개발자가 명시적으로 처리해야 한다.
- catch 혹은 throws 로 처리한다.
- throws 했다면 이후에 꼭 catch 해야한다.
- 만약, 처리하지 않으면 Compile 오류가 발생한다.
- catch 혹은 throws 로 처리한다.
- IOException, SQLException, ClassNotFoundException 등이 Checked Exception
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CheckedExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
readFile("example.txt");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IOException caught: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void readFile(String fileName) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
reader.close();
}
}// 위 예제에서 readFile 메서드는 파일을 읽는 동안 IOException이 발생할 수 있으므로, 메서드 선언에 throws IOException을 사용하여 이 예외를 던질 수 있음을 명시한다. main 메서드에서는 이 예외를 try-catch 블록으로 처리
Unchecked Exception
- RuntimeException과 하위 Exception
- 말그대로 Compiler가 체크하지 않는다.
- Unchecked Exception은 발생한 예외를 개발자가 명시적으로 처리하지 않아도 된다.
- throws를 생략할 수 있다. Checked Exception은 꼭 처리 해야됨
- NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException, IllegalArgumentException 등이 Unchecked Exception
public class UncheckedExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
divide(10, 0);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("ArithmeticException caught: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public static int divide(int a, int b) {
return a / b;
}
}// 위 예제에서 divide 메서드는 ArithmeticException을 던질 수 있으며, 이는 Unchecked Exception.
main 메서드에서는 이 예외를 try-catch 블록으로 처리
정리
- Checked Exception
- throws, catch 를 생략할 수 없다.
- Unchecked Exception
- throws, catch 를 생략할 수 있다.